
Then there are the stratosphere, thermosphere, and the very outer layer is the exosphere. Immediately above the surface is the troposphere. The “surface” of the planet is considered to be where the pressure is equal to sea level on Earth. Sometimes the concentrations are up to 100 times higher than at the poles.Īlso like the other gas giants, Neptune has no distinct firm surface.
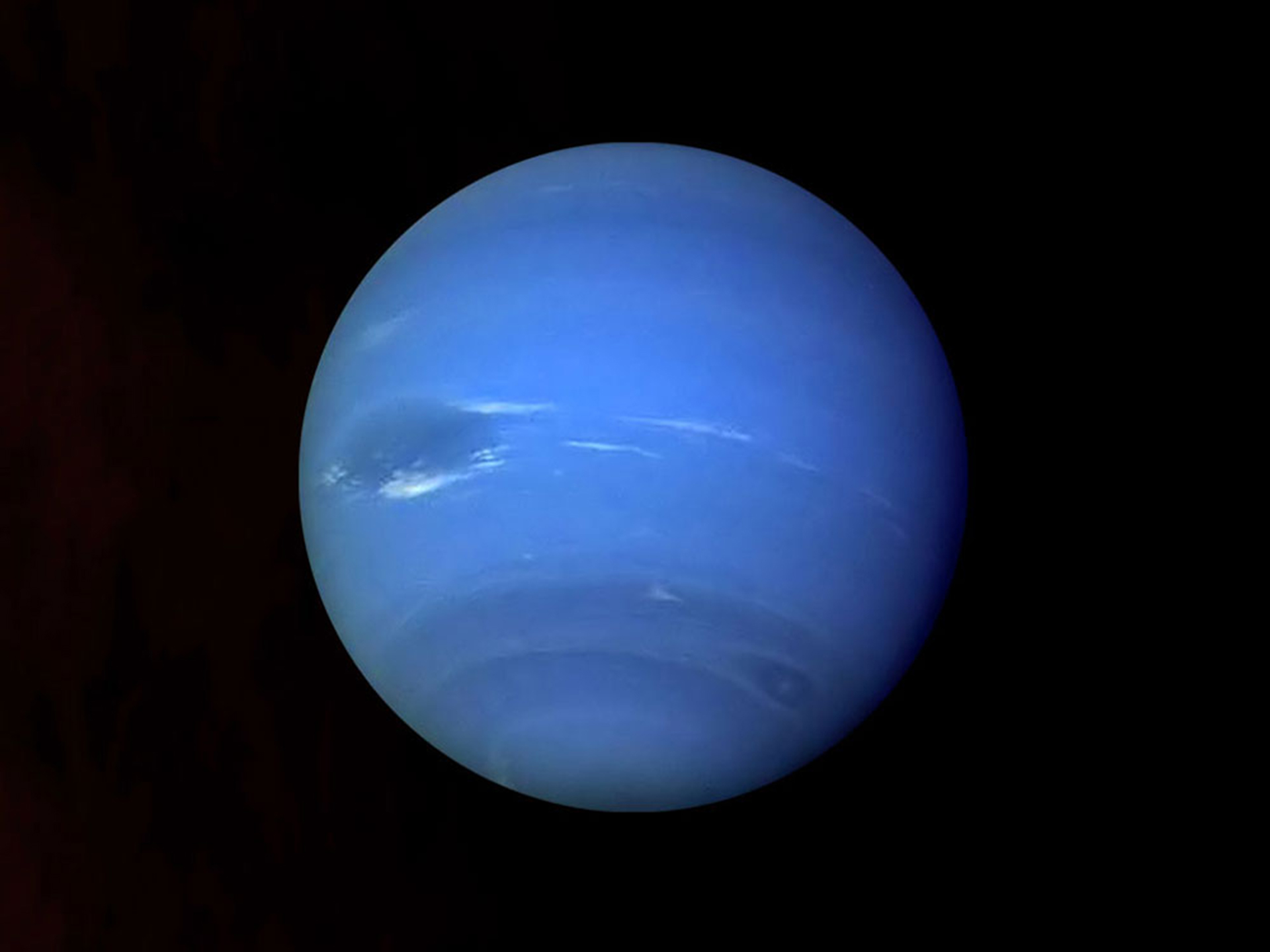

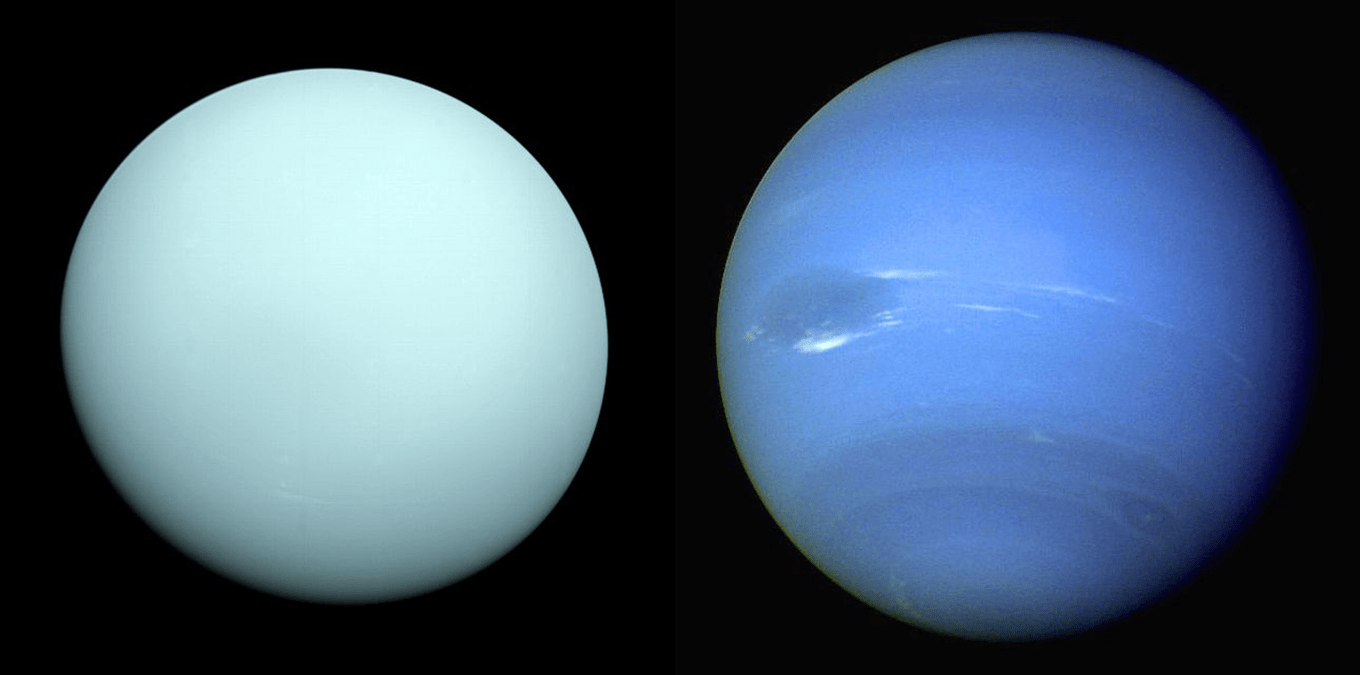
It has higher concentrations of methane, ethane and ethyne at its equator. Neptune and Uranus have similar compositions, but Neptune appears brighter and scientists are unsure why.ĭistribution of atmospheric particles on Neptune is interesting. This allows the blue light to bounce back, making the planet blue. The entire spectrum of light from the sun hits the planet, but the methane absorbs all of the light at the red end of the spectrum. The blue color that the planet is noted for is actually caused by the methane in the upper parts of the atmosphere. Neptune also has unique concentrations of methane. Neptune and Jupiter are farther from the sun and colder, allowing more ice to form. Unlike the gas giants, Saturn and Jupiter, Neptune’s atmosphere has large amounts of ice, making it more similar in that way to Uranus.

It also has trace amounts of methane and water. Like the other large planets, Neptune’s atmosphere is largely composed of helium and hydrogen. Neptune’s atmosphere has a lot in common with the atmospheres of all of the large gas planets in the Solar System, but it has a number of unique features, as well. Neptune is the eighth planet from the sun and has some of the most violent weather in the Solar System.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
